Empowering you to make better financial decisions, We truly are professional money planners...

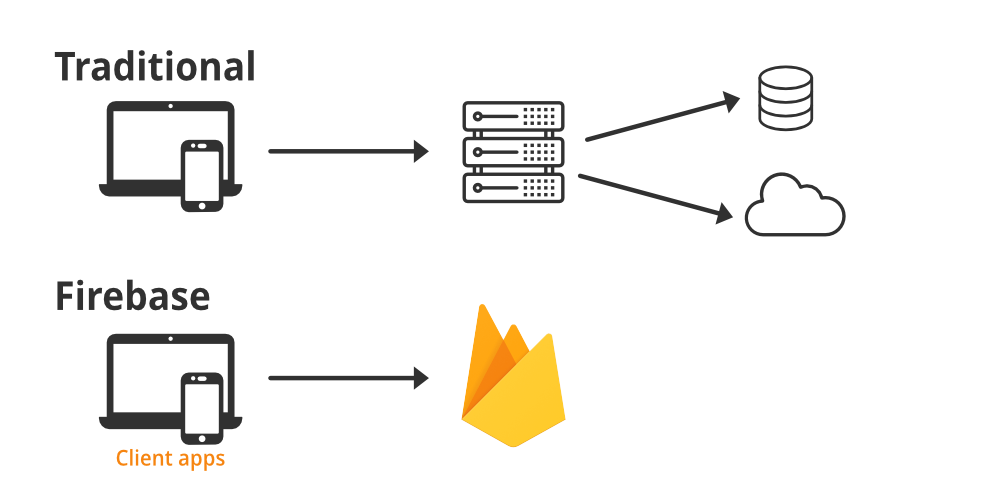
Firebase Realtime Database is a cloud-hosted NoSQL database that supports real-time data syncing across all clients. Below are the basic operations and examples on how to interact with Firebase Realtime Database.
Before using Firebase Realtime Database, ensure you have set up Firebase in your project.
Create a Firebase project in the Firebase Console.
Add Firebase SDK to your web project:
const firebaseConfig = { apiKey: "YOUR_API_KEY", authDomain: "your-project-id.firebaseapp.com", databaseURL: "https://your-project-id.firebaseio.com", projectId: "your-project-id", storageBucket: "your-project-id.appspot.com", messagingSenderId: "your-messaging-sender-id", appId: "your-app-id", };
Add the Firebase SDK to your HTML file:
<script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/9.6.1/firebase-app.js"></script> <script src="https://www.gstatic.com/firebasejs/9.6.1/firebase-database.js"></script> <script> // Initialize Firebase const app = firebase.initializeApp(firebaseConfig); const database = firebase.database(app); </script>
You can write data to Firebase using the set() and push() methods.
set() to Write DataThe set() method will overwrite the data at the specific reference.
// Reference to the database location const dbRef = firebase.database().ref("users/"); // Set data at the 'users' reference dbRef.set({ user1: { name: "John Doe", email: "john.doe@example.com", age: 30, }, user2: { name: "Jane Doe", email: "jane.doe@example.com", age: 28, }, });